Ancient York Cemetery Sheds Light on the Roman Empire
/Located approximately 300km north of London, the city of York was a major Roman outpost close to the northern border of their British domain. The area had been populated since approximately 7000 B.C., but the city itself was founded as Eboracum in 71 A.D. when it became a Roman fortress and settlement. For hundreds of years, the city was presided over by a series of emperors. However, after the fall of Rome, the city was overrun by the Angles in the 5th Century.
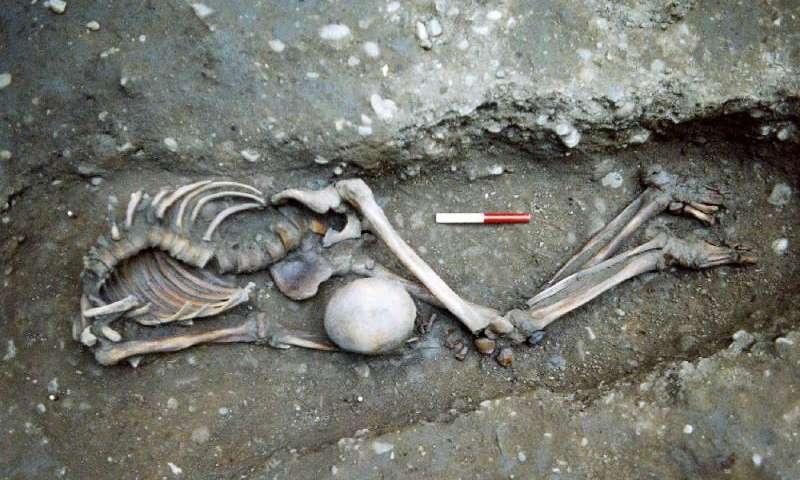
An ancient Roman cemetery was discovered in 2004 in the gardens of Driffield Terrace as they prepared to develop the property. The York Archeological Trust excavated the site and was more than a little surprised to find 80 sets of remains from the Roman period dating from the early second century to the late fourth century A.D. The cemetery is located on what would have been the outskirts of Eboracum, across the river from the Roman fort.
The remains were determined to be those of Roman gladiators based on several details. The bone structure of the individuals indicated that they were all men of less than forty-five years old and of large stature with heavy muscle attachment points, indicating a muscular physique. Remodeled bone told the tale of significant battle trauma and one set of remains even showed signs of a large animal bite, likely a lion or bear from the gladiatorial ring.
In 2010 testing was done on some of the bones based on strontium isotope analysis and it was determined that the individuals studied likely came from diverse areas and were not all of British origin. Of the eighteen individuals tested, only five came from York. The remaining thirteen came from outlying areas of Britain, mainland Europe and the parts of the Mediterranean, and the Middle East. Traces of carbon and nitrogen in the bones also led the team to the conclusion the gladiators ate a very different diet than the majority of the population of York, confirming the theory that they came from different geographical origins. A number of the skeletons had been decapitated and the skulls buried with them on their chest, between their legs, or at their feet.
However, at the time, scientific techniques to identify the exact origins of the men didn’t exist. But current day cutting-edge genome wide analysis now allows for the level of precision and analysis required to identify genealogical locations. Researchers from Trinity College Dublin selected seven skeletons for testing. Of these seven, six were found to be of British origin and related to the modern Welsh people, suggesting a migration from the area with the arrival of the Angles in the fifth century. The remaining skeleton however was radically different, and researchers matched his DNA sequences to the Middle East, specifically to Palestine, Jordan or Syria.
This is the first definitive evidence of the scope of the Roman Empire and the movement of troops within it. In a time where mobility of troops was an enormous proposition, it is clear that some of the centurions were very well travelled. The study also confirms the multi-ethnic composition of the Roman Empire.
Photo credit: York Archeological Trust





 COMPLETE!
COMPLETE! Planning
Planning